
He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries. He has been the CFO or controller of both small and medium sized companies and has run small businesses of his own. He has been a manager and an auditor with Deloitte, a big 4 accountancy firm, and holds a degree from Loughborough University. If the actual amount of overhead is different from the estimated amount used, the overhead is considered either over-absorbed or under-absorbed.
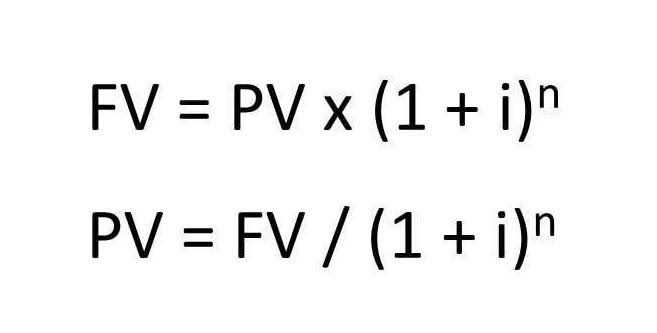
Semi-Variable Costs
- In a company, the management wants to calculate the predetermined overhead to set aside some amount for the allocation of a cost unit.
- The overhead is then applied to the cost of the product from the manufacturing overhead account.
- A predetermined overhead rate (POHR) is a rate that is used to allocate overhead costs to products or services.
- We’ll outline the basic formulas used to calculate different types of overhead rates and provide overhead cost examples.
- Predetermined overhead rates serve as benchmarks for evaluating the efficiency of manufacturing processes and overhead control.
- After going to its terms and conditions of the bidding, it stated the bid would be based on the overhead rate percentage.
First, they can help businesses to more accurately estimate the cost of their products or services. This can lead to more informed decision-making about pricing and production levels. In this article, we will cover how to calculate the predetermined overhead rate. The predetermined overhead rate is also commonly called predetermined absorption rate or predetermined overhead absorption rate.

Accelerating Financial Closures
Therefore, they use labor hours for the apportionment of their manufacturing cost. Calculation of predetermined overhead rates enables manufacturers to set product prices that accurately reflect the production costs, safeguarding profit margins. By inputting basic cost and activity data, Sourcetable’s AI assistant instantly computes the overhead rate using the formula Total Estimated Overhead Costs / Total Estimated Allocation Base.
- By knowing the total overhead costs for a period in advance, businesses can plan for the necessary cash flow to cover these costs.
- The predetermined overhead rate is calculated by dividing the estimated manufacturing overhead by the estimated activity base (direct labor hours, direct labor dollars, or machine hours).
- The predetermined overhead rate plays a pivotal role in financial decision-making processes.
- To calculate the predetermined overhead rate (POR), begin by estimating the total manufacturing overhead costs for the upcoming reporting period.
- It is calculated by dividing the estimated total overhead costs for a period by the estimated number of units that will be produced or sold during that period.
- Forecast future overhead costs based on historical data, industry trends, and expected changes in production volume.
Step 3: Estimate Your Allocation Base
This could be machine hours, labor hours, or any other measure that reflects the use of manufacturing resources. This includes all costs related to the production process that are not direct materials or direct labor. Common components are the salaries of factory managers, factory rent, property taxes, and depreciation. The POR is used to apply overhead costs to products or job orders, helping businesses to accurately price their products, manage budgets, and analyze cost behavior. It’s particularly useful in scenarios where indirect costs are significant and need to be fairly allocated across different products or services.

Overhead rate is a ratio that measures overhead or indirect costs against direct costs, machine hours, or labor hours. If the estimated overhead is $15,000 and the machine hours are 25,000, the predetermined overhead rate is $0.60 per unit. The formula for calculating predetermined overhead rate is estimated overhead divided by the allocation base. A number of possible allocation bases are available for the denominator, such as direct labor hours, direct labor dollars, and Outsource Invoicing machine hours. Larger organizations may employ a different predetermined overhead rate in each production department, which tends to improve the accuracy of overhead application by employing a higher level of precision.
The most common types of activity used to calculate a POHR are direct labor hours, machine hours, and units produced. Direct labor hours measure the amount of time workers spend performing tasks directly related to producing goods or services. However, it may not accurately reflect overhead costs if direct labor hours are not a significant factor what is predetermined overhead rate in the production process.
When preparing their budget for next year, Vison can estimate machine hours that will be used and allocate overhead costs accordingly. The base used to apply overhead, such as labor hours, machine hours, or units produced. Predetermined overhead rates help organizations in crafting comprehensive budgets that incorporate both direct and indirect costs, and in setting financial targets and performance benchmarks.
What are the different types of activity bases that can be used to calculate a POHR?
Understanding how to calculate the predetermined overhead rate is vital for effective Accounting Periods and Methods cost management and resource allocation. By following these steps, businesses can efficiently allocate their manufacturing overhead to individual products or projects and make more informed management decisions. The ABC method involves identifying and assigning overhead costs to specific activities that are required to produce goods or services. It then divides the total overhead costs for each activity by the corresponding activity volume to derive the predetermined overhead rate for that activity. The ABC method is more complex than the traditional method but can provide more accurate and granular overhead cost allocation.
Machine Hour Rate

Next, you need to choose an allocation base that you will use to distribute the overhead among products or job orders. The allocation base should be a factor that has a relationship with the overhead expenses. Common allocation bases include direct labor hours, direct labor cost, and machine hours. The most common types of activity bases are direct labor hours, machine hours, and units produced.